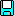
PB-1000 emulator
The program emulates the HD61700 microprocessor and uses the ROM dump from the original calculator, therefore it should function almost exactly like the real one.
It works on PC-compatible machines with Microsoft Windows operating system.
The main purpose of creating this program was the verification of the correctness of the reconstructed processor's internal ROM image, and to have a tool helping by the analysis of the ROM disassembly.
Program version 52, updated 2025/07/27
 pb1000es.zip - Delphi 5 sources
pb1000es.zip - Delphi 5 sources
 pb1000em.zip - compiled executable
pb1000em.zip - compiled executable
Usage: extract the files into an empty directory, then run the program pb1000.exe
 pb1000ej.zip - Japanese version
pb1000ej.zip - Japanese version
Usage: Replace the files rom1.bin and face.bmp in the directory where the program was installed.
 pb1000c.zip - version PB-1000C with CASL
pb1000c.zip - version PB-1000C with CASL
Usage: Replace the files rom1.bin and face.bmp in the directory where the program was installed.
- Following files contain the memory images, and are loaded when the program is started:
rom0.bin - processor's internal 6kB ROM
rom1.bin - external 32kB ROM
charset.bin - LCD controller's internal character ROM of size 1.5kB
ram0.bin - on-board 8kB RAM
ram1.bin - 32kB RAM in the expansion module
register.bin - processor's internal register file
- The updated files
ram0.bin, ram1.bin and register.bin are saved when the program is terminated.
If they weren't found, they will be created.
In such case the memory has to be initialised with the New All button.
- The emulator can be operated with the mouse or the keyboard.
Special function keys:
Cursor keys: corresponding membrane keys
Ctrl: [F]
Page Up: SHIFT
Page Down: CAPS
Esc: BRK
Insert: INS
Delete: DEL
Backspace: BS
Enter: EXE
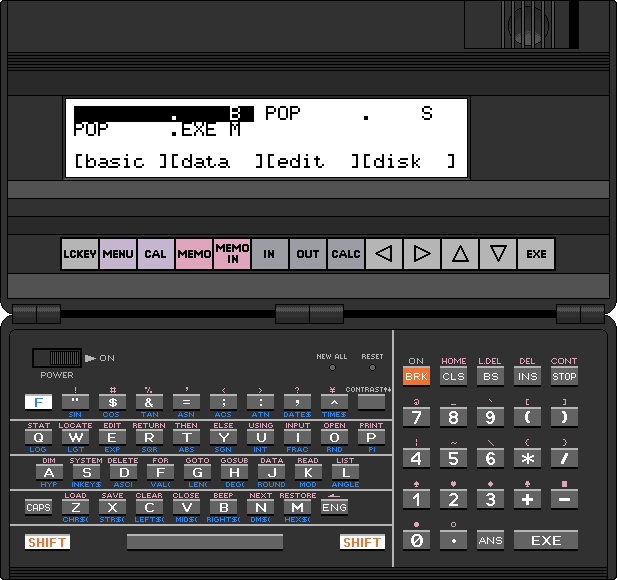
F3: suspends the code execution and opens the debugger window
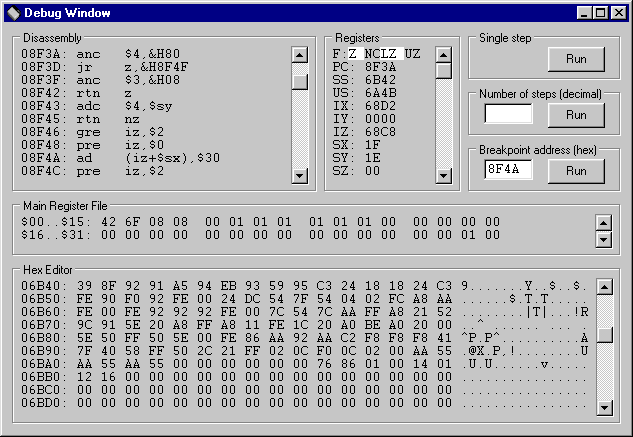
F4: invokes the communication utility
Shift+F4: selection of the floppy disk image file
To press two keys simultaneously, both the PC keyboard and the mouse must be used.
For example to type the ANGLE keyword either click on the [F] key on the screen and press the L on the PC keyboard, or hold the Ctrl key on the PC keyboard and click on the L key on the screen.
- A mouse click on the LCD area simulates the touch-screen function.
- The application can be closed by clicking on the cover lock on the upper-right edge of the form.
MD-100 compatible peripheral devices
Serial port
The communication utility invoked with the F4 key is equivalent to a terminal program used with a real calculator. Button functions:
- [Send]
- selects the file to be sent to the calculator
- [Receive]
- selects the file to which the data received from the calculator is saved
- [Stop]
- closes the file
Printer
The printed text is saved to the file selected with the [Receive] button of the communication utility.
Floppy disk drive
The floppy disk image file is specified in the INI file or can be selected with Shift+F4. The file disk0.bin included in the archive contains a sample floppy disk image. The size of this file determines the storage media capacity. An original floppy disk can hold 327680 bytes, but the file system can handle volumes up to 512 kilobytes. Its contents can be manipulated with the md100 utility written by Marcus von Cube.
Disassembly box
- On entry, the starting address matches the Program Counter, but it can be modified by clicking on the address in the first line.
New value must be confirmed with Enter.
- After clicking on a disassembled instruction, a new instruction can be typed.
As with the starting address, pressing Enter accepts the changes.
Only changes in the RAM area will be saved upon program termination, all ROM modifications will be lost.
Characteristics:
- labels and expressions aren't supported
- accepted are hexadecimal (with the prefix &H) and decimal numbers
- destination of relative jumps can be only specified as absolute address, not as displacement
Hex Editor box
- The HEX box allows viewing/changing the RAM contents only.
- It is possible to modify the starting address and the RAM contents by clicking on them.
Enter accepts the changes.
Registers box
- The contents of the registers can be modified by clicking on them.
Enter accepts the changes.
- The top line in the register box shows the state of the upper four bits of the Flag register.
They can be modified as well.
Main register file box
- The contents of the registers can be modified by clicking on them.
Enter accepts the changes.
Program execution control
- Closing the debugger windows resumes the program execution without tracing.
- Pressing the button [Run] in the Single step group box executes a single machine code instruction without servicing of the interrupts.
- To execute a specified number of machine code instructions type the required value to the field in the Number of steps group box, then press the associated [Run] button.
- The Breakpoint group box allows to specify condition that determine when the program execution should be interrupted.
Currently it only compares the Breakpoint Address typed in the field with the Program Counter.
When they match, the program execution is stopped and the debugger window reappears.
Some parameters of the emulator can be customised by editing the pb1000.ini file with any text editor.
Description of the contents of this file:
OscFreq = 910- This setting specifies the emulated CPU clock frequency in kHz.
DiskName = disk0.bin- This setting specifies the name the of the floppy disk image file. The full path can be provided as well.
To uninstall the emulator, simply delete the directory where it was installed.
The program doesn't modify anything outside its installation directory.
- The program includes a freeware component ThreadedTimer developed by Carlos Barbosa.
- The sound isn't supported yet.
- The scrolling function of the LCD controller command $8 isn't supported.
- Bugs may still lurk in the
rom0.bin memory image.
 pb1000et.zip - sources and executables, DOS and Windows (in a DOS window)
pb1000et.zip - sources and executables, DOS and Windows (in a DOS window)
This utility transfers files between the PC and the ramdisk area of the RAM image used by the emulator.
Usage:
ramtrans.exe [-n] <command> <options> <parameters>
- The program needs to be placed in the same directory as the RAM image files
ram0.bin and ram1.bin
- The ramdisk filenames are eight characters long plus three characters for a file extension.
They are case sensitive and can contain characters not allowed on the PC.
- Ramdisk patterns containing wildcards should be enclosed in quotes to avoid their expansion by the shell.
Command overview
- dir <options> <ramdisk-pattern>
-
- Displays a list of the files in the ramdisk directory.
If the pattern is specified, only files matching the pattern will be shown.
Examples:
- list all files: ramtrans dir
- list only selected files: ramtrans dir "*.BAS"
- type <options> <ramdisk-file>
-
- Displays the contents of a file either as hex dump or a text, depending on the file type (binary or ASCII).
BASIC programs can be decoded from their internal, tokenized form.
Examples:
- decoded BASIC program TEST.BAS:
ramtrans type -a TEST.BAS
- hex dump of all files with an extension .BIN:
ramtrans type -b "*.BIN"
- get <options> <ramdisk-file> [<pc-file>]
-
- Copies a single file from the ramdisk to the PC.
If the PC file name is not specified, the copied file is given the original name.
Examples:
- single file PI.BAS: ramtrans get -i pi.bas
- tokenized BASIC program PI.BAS as plain text:
ramtrans get -a -i pi.bas pi.txt
- mget <options> <ramdisk-pattern>
-
- Copies multiple files from the ramdisk to the PC.
Examples:
- multiple files to the local directory:
ramtrans mget "P*.BAS"
- multiple files to a specified PC directory (after the -d option):
ramtrans.exe mget -d c:\windows\temp\ "*.BIN"
- put <options> <pc-file> [<ramdisk-file>]
-
- Copies a single file from the PC to the ramdisk.
If the destination file name is not specified, the copied file is given the original name.
The file type should be set with the -t option, otherwise the program tries to guess it from the extension.
Example:
- option -u changes the destination name to upper case:
ramtrans put -u pi.asc
- mput <options> <pc-files>
-
- Similar to put, but copies multiple files.
- del <options> <ramdisk-pattern>
-
- Deletes files on the ramdisk.
- ren <options> <ramdisk-file> <new-name>
-
- Renames files on the ramdisk.
Options overview
- -i
- Ignore the case of ramdisk file(s).
- -l
- Make all files lowercase.
- -u
- Make all files uppercase.
It is convenient to select this option when transferring files to the ramdisk.
- -tX
- Select type to X (B, M, S or hex).
The PB-1000 files have an additional attribute (the file type) which is used for correct handling of a file selected from the menu:
- S - Sequential files, including MEMO files, assembly source files, files loaded via RS-232C and BASIC programs saved with SAVE,A.
The contents is ASCII text with CR+LF delimiters, terminated by Ctrl-Z.
- M - Machine code files (for example created by the built-in assembler) and binary files (for example created with BSAVE).
- B - BASIC programs in internal representation.
It is important to select proper type when transferring files to the ramdisk.
- -b
- Force binary transfer.
This option should be selected when transferring tokenized BASIC programs and binary files.
Note: the ramtrans utility doesn't preserve the information about the destination address and the start address of machine code programs.
Such task requires appropriate file formats (for example PBF) along with corresponding loaders (for example PBFTOBIN provided with the HD61 assembler).
- -a
- Force ASCII transfer.
This option should be selected to transfer PC text files, because it ensures correct line termination (CR+LF) and file termination (Ctrl-Z).
It's also suitable for machine code programs in PBF format.
- -n
- No updates are written to the RAM image, useful for testing.
It's an adaptation of the md100 utility written by Marcus von Cube, which performs similar operations, but on an MD-100 floppy disk or an image thereof.
![]() pb1000es.zip - Delphi 5 sources
pb1000es.zip - Delphi 5 sources![]() pb1000em.zip - compiled executable
pb1000em.zip - compiled executable![]() pb1000ej.zip - Japanese version
pb1000ej.zip - Japanese version![]() pb1000c.zip - version PB-1000C with CASL
pb1000c.zip - version PB-1000C with CASL


![]() pb1000et.zip - sources and executables, DOS and Windows (in a DOS window)
pb1000et.zip - sources and executables, DOS and Windows (in a DOS window)